Alexander, Sarah;
Braisher, Marie;
Tur, Carmen;
Chataway, Jeremy;
(2022)
The mSteps pilot study: Analysis of the distance walked using a novel smartphone application in multiple sclerosis.
Multiple Sclerosis Journal
, 28
(14)
pp. 2285-2293.
10.1177/13524585221124043.

Preview |
Text (Article)
Chataway_2_Clean_The mSteps pilot study- analysis of the distance walked using a novel smart-phone application, in multiple sclerosis_MSJ.pdf Download (258kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Table 1)
3_Table 1_MSJ.pdf Download (93kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Table 2)
3_Table 2_MSJ.pdf Download (88kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Table 3)
3_Table 3_MSJ.pdf Download (107kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Figure Legend)
4_Figure Legends_MSJ.pdf Download (59kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 1]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/6.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%201_MSJ.jpg)  Preview |
Image (Image 1)
5_Figure 1_MSJ.jpg Download (323kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Image (Image 2)
5_Figure 2_MSJ.tiff Download (1MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 3]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/8.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%203_MSJ.jpg) 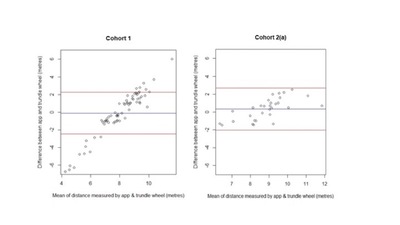 Preview |
Image (Image 3)
5_Figure 3_MSJ.jpg Download (45kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 4]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/9.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%204_MSJ.jpeg) 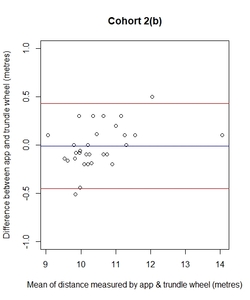 Preview |
Image (Image 4)
5_Figure 4_MSJ.jpeg Download (70kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 5]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/16.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%205_MSJ.jpeg) 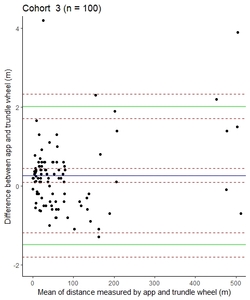 Preview |
Image (Image 5)
5_Figure 5_MSJ.jpeg Download (103kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 6a]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/10.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%206a_MSJ.jpeg) 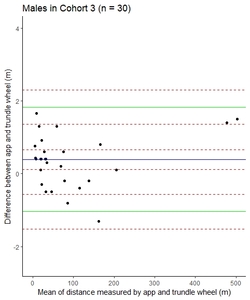 Preview |
Image (Image 6a)
5_Figure 6a_MSJ.jpeg Download (97kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 6b]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/11.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%206b_MSJ.jpeg) 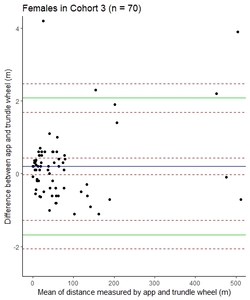 Preview |
Image (Image 6b)
5_Figure 6b_MSJ.jpeg Download (103kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 6c]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/12.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%206c_MSJ.jpeg) 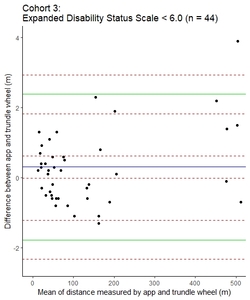 Preview |
Image (Image 6c)
5_Figure 6c_MSJ.jpeg Download (112kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 6d]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/13.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%206d_MSJ.jpeg) 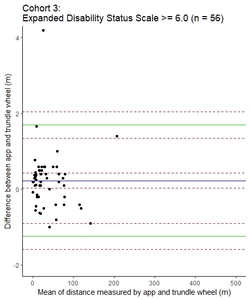 Preview |
Image (Image 6d)
5_Figure 6d_MSJ.jpeg Download (110kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 6e]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/14.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%206e_MSJ.jpeg) 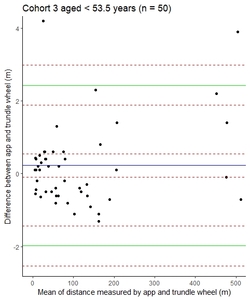 Preview |
Image (Image 6e)
5_Figure 6e_MSJ.jpeg Download (105kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Image 6f]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10165903/15.hassmallThumbnailVersion/5_Figure%206f_MSJ.jpeg) 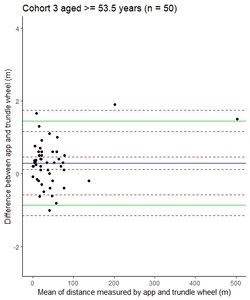 Preview |
Image (Image 6f)
5_Figure 6f_MSJ.jpeg Download (104kB) | Preview |
Abstract
Background: Clinical studies in multiple sclerosis (MS) often require accurate measurement of walking distance. Utilisation of electronic devices could theoretically improve this. Mobile devices have the potential to continuously monitor health by collecting movement data. Popular fitness trackers record steps taken and distance travelled, typically using a fixed-stride length. However, applications using fixed-stride length may be less accurate in those with altered gait patterns. While useful for everyday purposes, medical monitoring requires greater accuracy. Objective: Our aim was to determine the agreement and reliability of using a smartphone application to measure distance walked. Method: A phone application (mSteps) was developed and tested in a pilot study and then a validation study, looking at an indoor and outdoor setting with people with multiple sclerosis (PwMS) and a control cohort. Results: In the pilot study, the 95% limits of agreement (LOA) for outdoor tracking in control cohort lay within the a priori defined limit; however, the indoor tracking in both cohorts did not meet the defined limit. The app was then successfully validated outdoors in PwMS. Conclusion: mSteps could be used to accurately measure distance outdoors in PwMS. There is still a need for solutions to accurately and reliably measure distance walked indoors.
Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |


