Bologna, M;
Paparella, G;
Fabbrini, A;
Leodori, G;
Rocchi, L;
Hallett, M;
Berardelli, A;
(2016)
Effects of cerebellar theta-burst stimulation on arm and neck movement kinematics in patients with focal dystonia.
Clinical Neurophysiology
, 127
(11)
pp. 3472-3479.
10.1016/j.clinph.2016.09.008.

Preview |
Text
Rocchi_2_Bologna et al., 2016 Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_Abstract_CLINPH R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (85kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Rocchi_2_Bologna et al., 2016 Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_Manuscript_CLINPH_R1_R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (263kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Rocchi_3_Bologna et a., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Table 1 R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (9kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Rocchi_4_Bologna et al, 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Table 2 R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (29kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Rocchi_5_Bologna et al, 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Table 3 R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (17kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Rocchi_6_Bologna et al., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Figure 1_MEP 300 dpi_R1.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1567918/33.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Rocchi_6_Bologna%20et%20al.%2C%202016_Cerebellar%20cTBS%20dystonia_CLINPH_Figure%201_MEP%20300%20dpi_R1.jpg)  Preview |
Image
Rocchi_6_Bologna et al., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Figure 1_MEP 300 dpi_R1.jpg - Accepted Version Download (570kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Rocchi_7_Bologna et al., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Figure 2_CS 300 dpi R1.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1567918/38.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Rocchi_7_Bologna%20et%20al.%2C%202016_Cerebellar%20cTBS%20dystonia_CLINPH_Figure%202_CS%20300%20dpi%20R1.jpg) 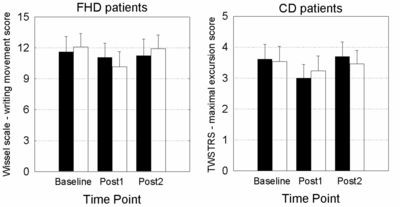 Preview |
Image
Rocchi_7_Bologna et al., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Figure 2_CS 300 dpi R1.jpg - Accepted Version Download (189kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Rocchi_8_Bologna et al., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Suppl.Table1 R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (12kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Rocchi_9_Bologna et al., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Supp.Table2 R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (106kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Rocchi_10_Bologna et al., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Supp.Table3 R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (92kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Rocchi_11_Bologna et al., 2016_Cerebellar cTBS dystonia_CLINPH_Suppl. Results R1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (165kB) | Preview |
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the cerebellar inhibitory influence on the primary motor cortex in patients with focal dystonia using a cerebellar continuous theta-burst stimulation protocol (cTBS) and to evaluate any relationship with movement abnormalities. METHODS: Thirteen patients with focal hand dystonia, 13 patients with cervical dystonia and 13 healthy subjects underwent two sessions: (i) cTBS over the cerebellar hemisphere (real cTBS) and (ii) cTBS over the neck muscles (sham cTBS). The effects of cerebellar cTBS were quantified as excitability changes in the contralateral primary motor cortex, as well as possible changes in arm and neck movements in patients. RESULTS: Real cerebellar cTBS reduced the excitability in the contralateral primary motor cortex in healthy subjects and in patients with cervical dystonia, though not in patients with focal hand dystonia. There was no correlation between changes in primary motor cortex excitability and arm and neck movement kinematics in patients. There were no changes in clinical scores or in kinematic measures, after either real or sham cerebellar cTBS in patients. CONCLUSIONS: The reduced cerebellar inhibitory modulation of primary motor cortex excitability in focal dystonia may be related to the body areas affected by dystonia as opposed to being a widespread pathophysiological abnormality. SIGNIFICANCE: The present study yields information on the differential role played by the cerebellum in the pathophysiology of different focal dystonias.
| Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Title: | Effects of cerebellar theta-burst stimulation on arm and neck movement kinematics in patients with focal dystonia |
| Open access status: | An open access version is available from UCL Discovery |
| DOI: | 10.1016/j.clinph.2016.09.008 |
| Publisher version: | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2016.09.008 |
| Language: | English |
| Additional information: | This version is the author accepted manuscript. For information on re-use, please refer to the publisher’s terms and conditions. |
| Keywords: | Science & Technology, Life Sciences & Biomedicine, Clinical Neurology, Neurosciences, Neurosciences & Neurology, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, Dystonia, Cerebellum, Motor Control, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, Toxin Type-A, Cervical Dystonia, Writers Cramp, Motor Cortex, Hand Dystonia, Basal Ganglia, Excitability, Circuits, Connectivity |
| UCL classification: | UCL UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Brain Sciences UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Brain Sciences > UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology |
| URI: | https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1567918 |
 Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading...Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |




