Murphy, DC;
Katta, M;
Egan, CA;
Michaelides, M;
Wickham, L;
(2022)
Long-term vision outcomes for patients with albinism and diabetic retinopathy.
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology
, 260
pp. 2165-2173.
10.1007/s00417-021-05313-x.

Preview |
Text (Accepted manuscript)
Michaelides_Revised ocular albinism and retinop V7.1 clean.pdf Download (178kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Image (Figure 1)
Michaelides_Figure 1 - between difference Va.tif Download (37kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 2]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10149511/4.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Michaelides_figure%202%20-%20patient%201%20300dpi.jpg)  Preview |
Image (Figure 2)
Michaelides_figure 2 - patient 1 300dpi.jpg Download (73kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 3]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10149511/5.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Michaelides_figure%203%20-%20patient%202%20300.jpg) 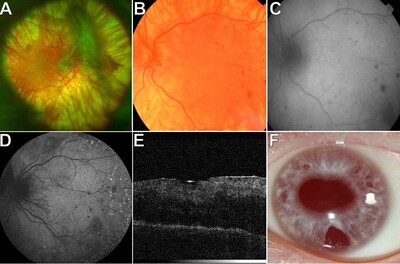 Preview |
Image (Figure 3)
Michaelides_figure 3 - patient 2 300.jpg Download (176kB) | Preview |
Abstract
Purpose: Albinism defines a group of genetic diseases which result from disordered melanin biosynthesis. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) results from poorly controlled type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and can lead to blindness due to progressive neovascularisation. However, the treatment of PDR in patients with ocular/oculocutaneous albinism may be more challenging. In this study, we compared a group of patients with albinism and PDR, to a group with albinism and diabetes mellitus but no PDR, to examine the long-term implications. // Methods: Retrospective observational study included all patients with ocular albinism (OA) or oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) and DM who presented at a single specialist centre. Participants were allocated into either group 1 (eyes with PDR) or group 2 (all eyes without PDR). Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS V26.0. Between-group differences were investigated. // Results: Outcome data was available for 5 eyes from 3 participants in group 1 and 26 eyes from 13 participants in group 2. Despite interventions, a large and significant difference in vision at follow-up was observed between group 1 and group 2 (mean change in visual acuity: 1.11 (± 1.00) versus − 0.15 (± 0.46), respectively; p = < 0.0001). // Conclusion: PDR is associated with poor long-term prognosis despite interventions for patients with albinism. Those without PDR appear to maintain stable vision. Alternative treatments for PDR and its complications may be required in this population. Measures to prevent the development of diabetic eye disease and progression towards PDR should be employed at an early stage.
| Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Title: | Long-term vision outcomes for patients with albinism and diabetic retinopathy |
| Location: | Germany |
| Open access status: | An open access version is available from UCL Discovery |
| DOI: | 10.1007/s00417-021-05313-x |
| Publisher version: | https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05313-x |
| Language: | English |
| Additional information: | This version is the author accepted manuscript. For information on re-use, please refer to the publisher's terms and conditions. |
| Keywords: | Albinism, Diabetes, Diabetic retinopathy, Ocular albinism |
| UCL classification: | UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Brain Sciences UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Brain Sciences > Institute of Ophthalmology UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences UCL |
| URI: | https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10149511 |
 Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading...Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |




