Hussein, M;
Alzoubaidi, D;
De la Serna, A;
Weaver, M;
Fernandez-Sordo, JO;
Rey, JW;
Hayee, B;
... Haidry, R; + view all
(2020)
Outcomes of Hemospray therapy in the treatment of intraprocedural upper gastrointestinal bleeding post-endoscopic therapy.
United European Gastroenterology Journal
10.1177/2050640620938549.
(In press).

Preview |
Text (Article)
Lovat_Hemospray post Endotherapy main document (without tables and figures) UEG ammendment 2.pdf - Accepted Version Download (574kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Table 1)
Lovat_Table 1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (344kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Table 1 - supplementary material)
Lovat_Table 1s Supplementary material table.pdf - Accepted Version Download (326kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Table 2)
Lovat_Table 2.pdf - Accepted Version Download (338kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Table 3)
Lovat_Table 3.pdf - Accepted Version Download (336kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Table 4)
Lovat_Table 4.pdf - Accepted Version Download (331kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 1]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10103192/69.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Lovat_Figure%201.png) 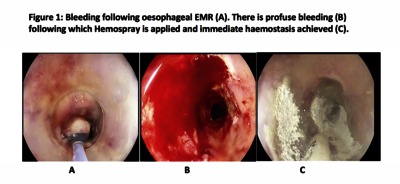 Preview |
Image (Figure 1)
Lovat_Figure 1.png - Accepted Version Download (1MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 2]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10103192/74.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Lovat_Figure%202.png) 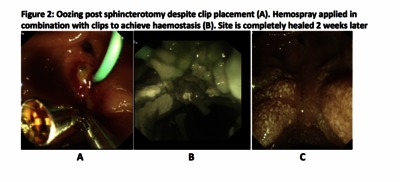 Preview |
Image (Figure 2)
Lovat_Figure 2.png - Accepted Version Download (1MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 3]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10103192/79.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Lovat_Figure%203%20UEG%20revision.png) 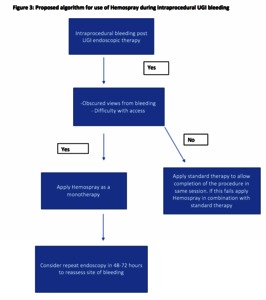 Preview |
Image (Figure 3)
Lovat_Figure 3 UEG revision.png - Accepted Version Download (346kB) | Preview |
Abstract
INTRODUCTION: With increasing advances in minimally invasive endoscopic therapies and endoscopic resection techniques for luminal disease, there is an increased risk of post-procedure bleeding. This can contribute to significant burden on patient's quality of life and health resources when reintervention is required. Hemospray (Cook Medical, North Carolina, USA) is a novel haemostatic powder licensed for gastrointestinal bleeding. The aim of this single-arm, prospective, non-randomised multicentre international study is to look at outcomes in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeds following elective endoscopic therapy treated with Hemospray to achieve haemostasis. METHODS: Data was prospectively collected on the use of Hemospray from 16 centres (January 2016-November 2019). Hemospray was used during the presence of progressive intraprocedural bleeding post-endoscopic therapy as a monotherapy, dual therapy with standard haemostatic techniques or rescue therapy once standard methods had failed. Haemostasis was defined as the cessation of bleeding within 5 min of the application of Hemospray. Re-bleeding was defined as a sustained drop in haemoglobin (>2 g/l), haematemesis or melaena with haemodynamic instability after the index endoscopy. RESULTS: A total of 73 patients were analysed with bleeding post-endoscopic therapy. The median Blatchford score at baseline was five (interquartile range 0-9). The median Rockall score was six (interquartile range 5-7). Immediate haemostasis following the application of Hemospray was achieved in 73/73 (100%) of patients. Two out of 57 (4%) had a re-bleed post-Hemospray, one was following oesophageal endoscopic mucosal resection and the other post-duodenal endoscopic mucosal resection. Both patients had a repeat endoscopy and therapy within 24 h. Re-bleeding data was missing for 16 patients, and mortality data was missing for 14 patients. There were no adverse events recorded in association with the use of Hemospray. CONCLUSION: Hemospray is safe and effective in achieving immediate haemostasis following uncontrolled and progressive intraprocedural blood loss post-endoscopic therapy, with a low re-bleed rate.
 Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading... Loading...
Loading...Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |




