Gastine, S;
Rashed, AN;
Hsia, Y;
Jackson, C;
Barker, CIS;
Mathur, S;
Tomlin, S;
... Sharland, M; + view all
(2019)
GAPPS (Grading and Assessment of Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Studies) a critical appraisal system for antimicrobial PKPD studies - development and application in pediatric antibiotic studies.
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology
, 12
(12)
pp. 1091-1098.
10.1080/17512433.2019.1695600.

Preview |
Text
Jackson_Antibiotic PK Evidence Assessment_1stRevision_wAuthor.pdf - Accepted Version Download (620kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Jackson_Supplement.pdf - Accepted Version Download (357kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Jackson_Figure_1.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10092535/13.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Jackson_Figure_1.jpg) 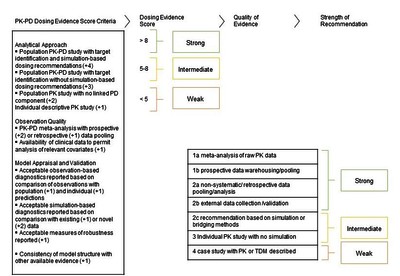 Preview |
Image
Jackson_Figure_1.jpg - Accepted Version Download (137kB) | Preview |
|
Other (Supporting information)
Jackson_Figure_2.eps - Accepted Version Download (6kB) |
|
|
Other (Supporting information)
Jackson_Figure_3.eps - Accepted Version Download (17kB) |
|
|
Other (Supporting information)
Jackson_Figure_4.eps - Accepted Version Download (7kB) |
Abstract
Introduction: There are limited data on optimal dosing of antibiotics in different age groups for neonates and children. Clinicians usually consult pediatric formularies or online databases for dose selection, but these have variable recommendations, are usually based on expert opinion and are not graded based on the existing pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PKPD) studies. We describe here a potential new tool that could be used to grade the strength of evidence emanating from PKPD studies. Areas covered: A scoring system was developed (GAPPS tool) to quantify the strength of each PK assessment and rate the studies quality in already published articles. GAPPS was evaluated by applying it to pediatric PKPD studies of antibiotics from the 2019 Essential Medicines List for children (EMLC), identified through a search of PubMed. Expert opinion: Evidence for most antibiotic dose selection decisions was generally weak, coming from individual PK studies and lacked PKPD modeling and simulations. However, the quality of evidence appears to have improved over the last two decades. Incorporating a formal grading system, such as GAPPS, into formulary development will provide a transparent tool to support decision-making in clinical practice and guideline development, and guide PKPD authors on study designs most likely to influence guidelines.
Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |


