Horikoshi, M;
Beaumont, RN;
Day, FR;
Warrington, NM;
Kooijman, MN;
Fernandez-Tajes, J;
Feenstra, B;
... Freathy, RM; + view all
(2016)
Genome-wide associations for birth weight and correlations with adult disease.
Nature
, 538
(7624)
pp. 248-252.
10.1038/nature19806.

Preview |
Text (Article)
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_MainText.FINAL.pdf - Accepted Version Download (720kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Supplementary data)
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_SupData.FINAL.pdf - Accepted Version Download (4MB) | Preview |
|
Spreadsheet
Hypponen_McCarthy_SupTable17.FINAL.xlsx - Accepted Version Download (134kB) |
|
Preview |
Text
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_SupTablesNotes.FINAL.pdf - Accepted Version Download (2MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure1.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/20.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure1.jpg) 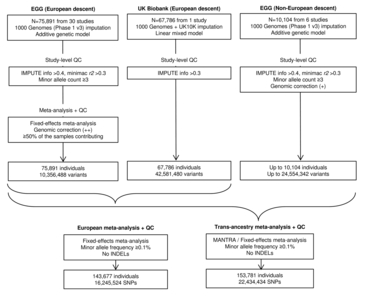 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure1.jpg - Accepted Version Download (498kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure2.jpeg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/26.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure2.jpeg) 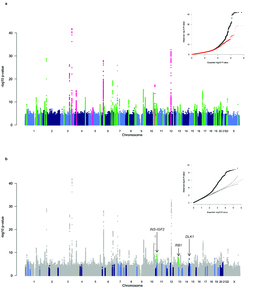 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure2.jpeg - Accepted Version Download (1MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure3.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/31.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure3.jpg) 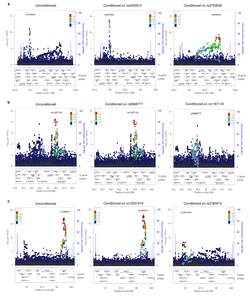 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure3.jpg - Accepted Version Download (1MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure4.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/36.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure4.jpg) 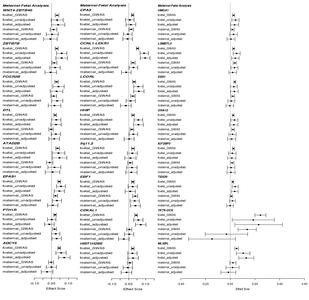 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure4.jpg - Accepted Version Download (911kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure5.jpeg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/41.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure5.jpeg)  Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure5.jpeg - Accepted Version Download (974kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure6.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/46.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure6.jpg) 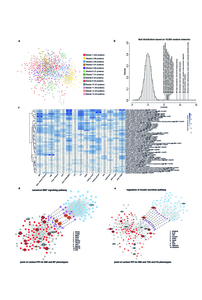 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure6.jpg - Accepted Version Download (6MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure7.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/51.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure7.jpg) 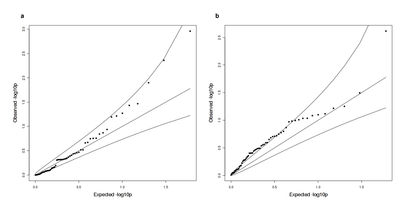 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure7.jpg - Accepted Version Download (228kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure8.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/56.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure8.jpg) 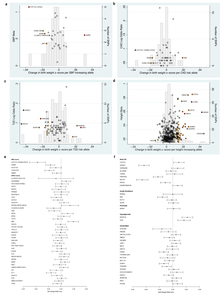 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataFigure8.jpg - Accepted Version Download (638kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataTable1.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/61.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataTable1.jpg) 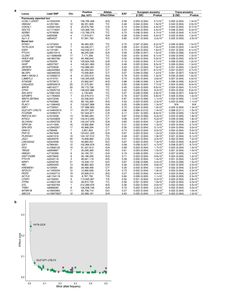 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataTable1.jpg - Accepted Version Download (1MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataTable2.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1521670/66.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataTable2.jpg) 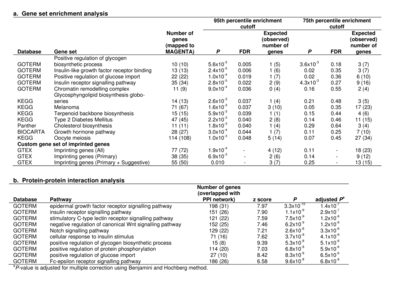 Preview |
Image
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_ExtendedDataTable2.jpg - Accepted Version Download (845kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_Figure1.pdf - Accepted Version Download (11kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Hypponen_McCarthyFreathy_Figure2.pdf - Accepted Version Download (2MB) | Preview |
Abstract
Birth weight (BW) has been shown to be influenced by both fetal and maternal factors and in observational studies is reproducibly associated with future risk of adult metabolic diseases including type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cardiovascular disease1. These life-course associations have often been attributed to the impact of an adverse early life environment. Here, we performed a multi-ancestry genome-wide association study (GWAS) meta-analysis of BW in 153,781 individuals, identifying 60 loci where fetal genotype was associated with BW (P < 5 × 10−8). Overall, approximately 15% of variance in BW was captured by assays of fetal genetic variation. Using genetic association alone, we found strong inverse genetic correlations between BW and systolic blood pressure (Rg = −0.22, P = 5.5 × 10−13), T2D (Rg = −0.27, P = 1.1 × 10−6) and coronary artery disease (Rg = −0.30, P = 6.5 × 10−9). In addition, using large -cohort datasets, we demonstrated that genetic factors were the major contributor to the negative covariance between BW and future cardiometabolic risk. Pathway analyses indicated that the protein products of genes within BW-associated regions were enriched for diverse processes including insulin signalling, glucose homeostasis, glycogen biosynthesis and chromatin remodelling. There was also enrichment of associations with BW in known imprinted regions (P = 1.9 × 10−4). We demonstrate that life-course associations between early growth phenotypes and adult cardiometabolic disease are in part the result of shared genetic effects and identify some of the pathways through which these causal genetic effects are mediated.
| Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Title: | Genome-wide associations for birth weight and correlations with adult disease |
| Open access status: | An open access version is available from UCL Discovery |
| DOI: | 10.1038/nature19806 |
| Publisher version: | http://doi.org/10.1038/nature19806 |
| Language: | English |
| Additional information: | This version is the author accepted manuscript. For information on re-use, please refer to the publisher’s terms and conditions. |
| Keywords: | Metabolic disorders, Quantitative trait, Intrauterine growth, Hypertension, Genome-wide association studies |
| UCL classification: | UCL UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Population Health Sciences > UCL GOS Institute of Child Health UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Population Health Sciences > UCL GOS Institute of Child Health > Population, Policy and Practice Dept |
| URI: | https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1521670 |
Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |


