Jardine, M;
Zhou, Z;
Lambers Heerspink, HJ;
Hockham, C;
Li, Q;
Agarwal, R;
Bakris, GL;
... Perkovic, V; + view all
(2021)
Kidney, Cardiovascular, and Safety Outcomes of Canagliflozin according to Baseline Albuminuria: A CREDENCE Secondary Analysis.
Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
, 16
(2)
, Article 15260920. 10.2215/CJN.15260920.

Preview |
Text (Accepted Manuscript)
Wheeler_Kidney, Cardiovascular, and Safety Outcomes of Canagliflozin according to Baseline Albuminuria- A CREDENCE Secondary Analysis_AAM.pdf - Accepted Version Download (391kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text (Supplementary Material)
Wheeler_Kidney, Cardiovascular, and Safety Outcomes of Canagliflozin according to Baseline Albuminuria- A CREDENCE Secondary Analysis_SuppM.pdf - Accepted Version Download (334kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure1_750dpi.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10123144/16.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure1_750dpi.jpg) 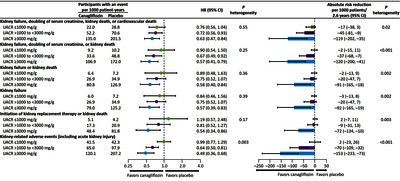 Preview |
Image
Figure1_750dpi.jpg - Accepted Version Download (405kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure2_750dpi.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10123144/21.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure2_750dpi.jpg)  Preview |
Image
Figure2_750dpi.jpg - Accepted Version Download (337kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure3_750dpi.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10123144/27.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure3_750dpi.jpg)  Preview |
Image
Figure3_750dpi.jpg - Accepted Version Download (216kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure4_750dpi.jpg]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10123144/34.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure4_750dpi.jpg)  Preview |
Image
Figure4_750dpi.jpg - Accepted Version Download (225kB) | Preview |
Abstract
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The kidney protective effects of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors are greater in people with higher levels of albuminuria at treatment initiation. Whether this applies to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors is uncertain, particularly in patients with a very high urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR; ≥3000 mg/g). We examined the association between baseline UACR and the effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor, canagliflozin, on efficacy and safety outcomes in the Canagliflozin and Renal Endpoints in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation (CREDENCE) randomized controlled trial. DESIGN, SETTING, PARTICIPANTS, & MEASUREMENTS: The study enrolled 4401 participants with type 2 diabetes, an eGFR of 30 to <90 ml/min per 1.73 m2, and UACR of >300 to 5000 mg/g. Using Cox proportional hazards regression, we examined the relative and absolute effects of canagliflozin on kidney, cardiovascular, and safety outcomes according to a baseline UACR of ≤1000 mg/g (n=2348), >1000 to <3000 mg/g (n=1547), and ≥3000 mg/g (n=506). In addition, we examined the effects of canagliflozin on UACR itself, eGFR slope, and the intermediate outcomes of glycated hemoglobin, body weight, and systolic BP. RESULTS: Overall, higher UACR was associated with higher rates of kidney and cardiovascular events. Canagliflozin reduced efficacy outcomes for all UACR levels, with no evidence that relative benefits varied between levels. For example, canagliflozin reduced the primary composite outcome by 24% (hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.56 to 1.04) in the lowest UACR subgroup, 28% (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.56 to 0.93) in the UACR subgroup >1000 to <3000 mg/g, and 37% (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.47 to 0.84) in the highest subgroup (Pheterogeneity=0.55). Absolute risk reductions for kidney outcomes were greater in participants with higher baseline albuminuria; the number of primary composite events prevented across ascending UACR categories were 17 (95% CI, 3 to 38), 45 (95% CI, 9 to 81), and 119 (95% CI, 35 to 202) per 1000 treated participants over 2.6 years (Pheterogeneity=0.02). Rates of kidney-related adverse events were lower with canagliflozin, with a greater relative reduction in higher UACR categories. CONCLUSIONS: Canagliflozin safely reduces kidney and cardiovascular events in people with type 2 diabetes and severely increased albuminuria. In this population, the relative kidney benefits were consistent over a range of albuminuria levels, with greatest absolute kidney benefit in those with an UACR ≥3000 mg/g. CLINICAL TRIAL REGISTRY NAME AND REGISTRATION NUMBER: ClinicalTrials.gov: CREDENCE, NCT02065791. PODCAST: This article contains a podcast at https://www.asn-online.org/media/podcast/CJASN/2021_02_22_CJN15260920_final.mp3.
| Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Title: | Kidney, Cardiovascular, and Safety Outcomes of Canagliflozin according to Baseline Albuminuria: A CREDENCE Secondary Analysis |
| Location: | United States |
| Open access status: | An open access version is available from UCL Discovery |
| DOI: | 10.2215/CJN.15260920 |
| Publisher version: | https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.15260920 |
| Language: | English |
| Additional information: | This version is the author accepted manuscript. For information on re-use, please refer to the publisher's terms and conditions. |
| Keywords: | SGLT2 inhibitors, albuminuria, canagliflozin, cardiovascular system, chronic kidney disease progression, diabetes, randomized controlled trials |
| UCL classification: | UCL UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Medical Sciences UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Medical Sciences > Div of Medicine UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Medical Sciences > Div of Medicine > Renal Medicine |
| URI: | https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10123144 |
Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |


