Mei, Z;
Han, Y;
Dong, L;
Turvey, ST;
Hao, Y;
Wang, K;
Wang, D;
(2019)
The impact of fisheries management practices on the survival of the Yangtze finless porpoise in China.
Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems
, 29
(4)
pp. 639-646.
10.1002/aqc.3078.

Preview |
Text (Article)
Mei_YFP-R1_Patrol_20181018.pdf - Accepted Version Download (161kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 1]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10066867/3.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig.%201.jpg) 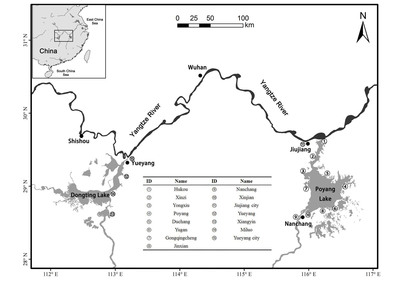 Preview |
Image (Figure 1)
Fig. 1.jpg - Accepted Version Download (163kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 2]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10066867/8.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig.%202.jpg) 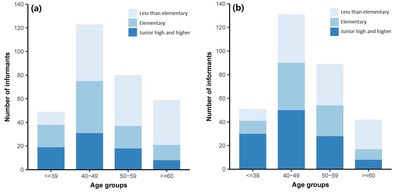 Preview |
Image (Figure 2)
Fig. 2.jpg - Accepted Version Download (119kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Image (Figure 3)
Fig_3.pdf - Accepted Version Download (132kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 4]](https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/10066867/21.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig.%204.jpg) 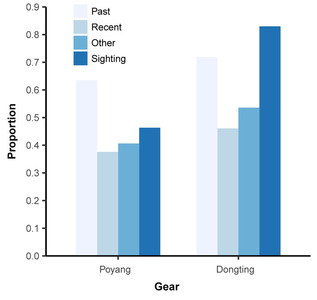 Preview |
Image (Figure 4)
Fig. 4.jpg - Accepted Version Download (84kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Image (Figure 5)
Fig_5.pdf - Accepted Version Download (130kB) | Preview |
Abstract
1. The Critically Endangered Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis) is facing a significant threat from illegal fishing in Poyang Lake and Dongting Lake, and current fisheries management has proved insufficient to eliminate illegal fishing. 2. A survey of local communities around the two lakes was conducted to investigate fishing activities and their potential impacts. Using a series of six scenarios derived from our data, we suggest that enhanced daytime patrols may have driven fishers to conduct compensatory night‐time fishing when the patrols are absent. Night‐time fishing activities overlap temporally with the main period of Yangtze finless porpoise foraging, so the potential intensification of night‐time fishing with the use of illegal gears could pose an increased threat to porpoises. 3. In addition to increasing law enforcement management efforts, helping fishers to secure alternative livelihoods may provide a more practical and sustainable long‐term method for reducing illegal fishing and its impacts on porpoises. This study also provides important lessons for conservation policy‐making and implementation for other cetacean species threatened by illegal fishing.
| Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Title: | The impact of fisheries management practices on the survival of the Yangtze finless porpoise in China |
| Open access status: | An open access version is available from UCL Discovery |
| DOI: | 10.1002/aqc.3078 |
| Publisher version: | http://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.3078 |
| Language: | English |
| Additional information: | This version is the author accepted manuscript. For information on re-use, please refer to the publisher’s terms and conditions. |
| Keywords: | freshwater cetacean; community interviews; insufficient conservation management; fisheries compensation; behavioural change; perverse effect |
| UCL classification: | UCL UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Life Sciences UCL > Provost and Vice Provost Offices > School of Life and Medical Sciences > Faculty of Life Sciences > Div of Biosciences |
| URI: | https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10066867 |
Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |


